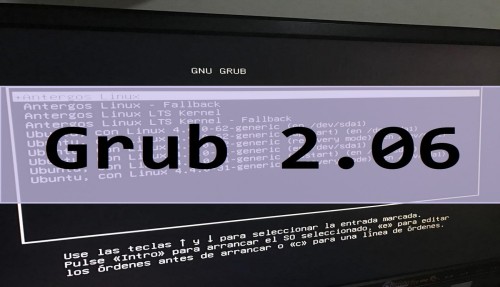
Grub (Grand Unified Bootloader) is a bootloader used to pass control of the startup process from the system firmware to the operating system. In other words, Grub is a program that tells your computer which operating system to boot from and how to configure it. On Linux systems, this typically includes loading a kernel, setting kernel arguments, and initiating the boot process.
Grub was originally created for the GNU Project, a free software project created in 1983 by Richard Stallman, who wanted to create a completely free operating system. Today, Grub has become a go-to for many Linux users due to its simple configuration, flexibility, and convenience. It is highly customizable, allowing users to select specific kernels and change parameters from the boot menu.
Grub is an essential part of the Linux operating system, as it takes care of the boot process and ensures that everything goes smoothly. Without Grub, you wouldn’t be able to start up a Linux machine. So the next time you turn on your computer and see that familiar boot screen, be sure to thank Grub!